Chikungunya Virus (Chikv) Wiki
Chikungunya virus is a virus transmitted through mosquito bites. Most people develop symptoms such as fever and joint pain within three to seven days after being bitten. Treatment mainly focuses on symptom control. Most patients start feeling better within a week.
What is Chikungunya Virus?
Chikungunya Virus (CHIKV) is a virus that spreads to people through mosquito bites — specifically, through the Aedes aegypti mosquito and Aedes albopictus mosquito. Chikungunya infection happens when a mosquito with the virus bites a person. The virus doesn’t spread from person to person through bodily contact or saliva, although blood transmission may be possible.
The virus is an RNA virus, classified under the Togaviridae family and the Alphavirus genus. The term “Chikungunya” originates from the Makonde language in southern Tanzania, meaning “that which bends,” describing the posture of those infected due to severe joint pain.
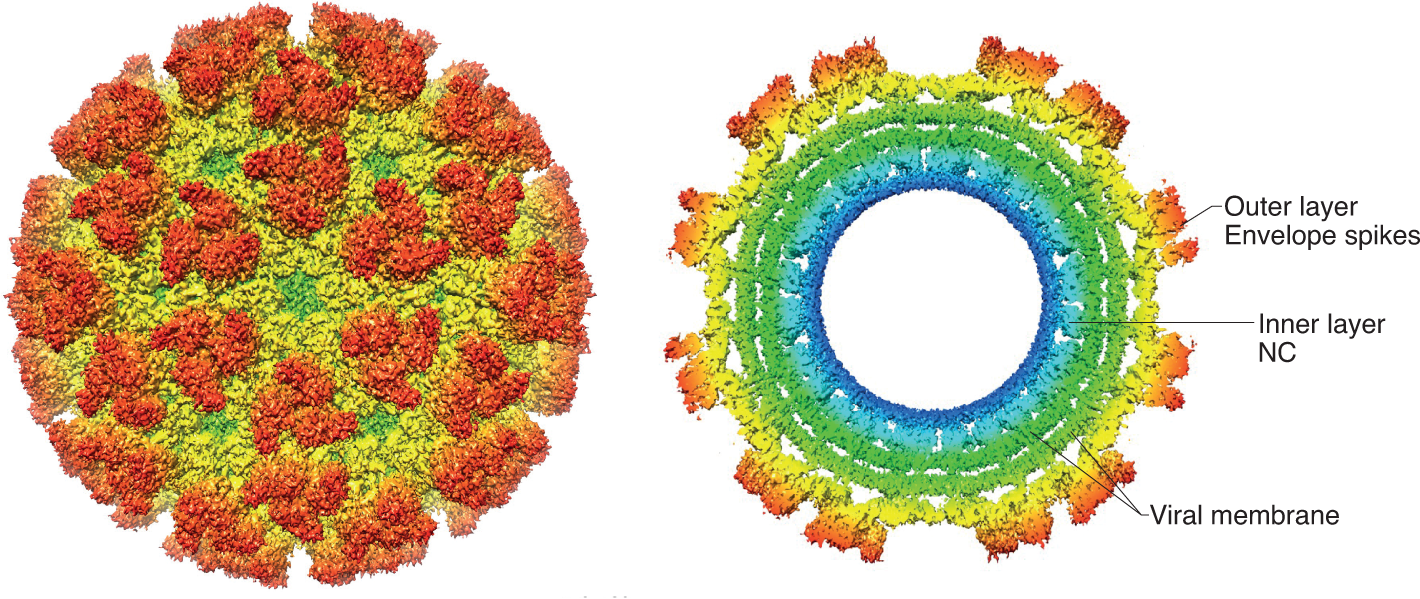
Chikungunya virus assembly and egress
What are the symptoms of Chikungunya Virus?
CHIKV disease onset is typically 4–8 days (range 2–12 days) after the bite of an infected mosquito. It is characterized by an abrupt onset of fever, frequently accompanied by severe joint pain. The joint pain is often debilitating and usually lasts for a few days but may be prolonged, lasting for weeks, months or even years. Other common signs and symptoms include joint swelling, muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue and rash. Since these symptoms overlap with other infections, including those with dengue and Zika viruses, cases can be misdiagnosed. In the absence of significant joint pain, symptoms in infected individuals are usually mild and the infection may go unrecognized.
Fever and joint pain are the most common symptoms of chikungunya virus. The intensity of symptoms can vary depending on the person. Many people feeling crippling joint pain. The fever usually begins suddenly. Some people can have such mild symptoms that they mistake the virus for another illness or don’t visit a healthcare provider.
Other symptoms could include:
- Headache.
- Muscle pain.
- Swelling in your joints.
- Rash.
- Fatigue.
- Nausea.
Most people’s symptoms will last about a week and then gradually fully recover. However, some may experience chronic joint pain after recovery.
How is Chikungunya Virus diagnosed?
If you experience symptoms of chikungunya fever and have recently traveled to areas known for chikungunya transmission, inform your healthcare provider. They can detect the chikungunya virus through methods such as reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or from blood samples collected. These tests are typically conducted during the first week after infection to check for viral antibodies. Antibody levels can usually be detected during the first week after onset and remain detectable for approximately 2 months.
How is Chikungunya Virus treated?
Clinical treatment includes using antipyretics and optimal pain relievers to alleviate fever and joint pain, drinking plenty of water, and resting. Currently, there is no specific antiviral drug treatment for CHIKV infections.
Most people feel better within a week after the onset of initial symptoms. However, some report that joint pain can persist for months or even years. Most evidence suggests that once infected with chikungunya, individuals are unlikely to be reinfected due to the immunity developed against the virus.
Notice: Taking acetaminophen for pain. Don’t take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) or aspirin until your healthcare provider makes a diagnosis.
Chikungunya Virus Transmission & contagious
How is Chikungunya Virus Transmission?
Chikungunya virus is transmitted by infected female mosquitoes, most commonly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, which can also spread dengue and Zika viruses.
Is Chikungunya Virus contagious?
People infected with the Chikungunya virus do not transmit the virus to others through bodily fluids such as saliva, sneezing, or coughing. The virus can only be spread through infected mosquitoes.
Who is most likely to get Chikungunya Virus?
You are most likely to contract the virus if you travel to a country with an ongoing outbreak or known transmission.
What are the complications of Chikungunya Virus?
The most common complication of this virus is chronic joint pain; after contracting chikungunya, the pain can last for months or even years. Newborns, elderly individuals (65 years or older), and those with certain health conditions may experience more severe complications due to the virus. These health conditions include: Diabetes, High blood pressure, Heart disease.
Latest situation
- 1

